PHP Version
Workspace uses the selected version of PHP to analyze the code, to provide specific code completions, to initiate built-in web server with debugging and profiling, and to run tests.
Status Bar
When editing a PHP code, the selected version of PHP is shown in the right part of the VS Code status bar, next to the "PHP" language mode.

Click on the version or run command > Select PHP version to open a quick picker with available PHP versions and your defined profiles (see the setting "php.executables"):
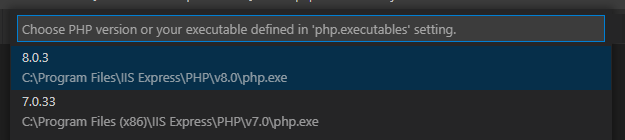
Selected version will be stored in the workspace "php.version" setting.

Setting php.version
The setting php.version specifies which PHP will be used within the current workspace. It can be either a full version string (e.g. "7.4.33), an identifier defined in php.executables below (e.g. "latest"), or a version prefix (e.g. "8" or "7.4").
Example:
{
"php.version": "8.0"
}This setting is automatically modified by the version picker initiated from the status bar above.
Setting php.executables
php.executables setting allows you to define custom paths to PHP binaries. Defined binaries will be also listed in the version picker.
Each executable has a unique name, which will be used to identify the PHP binary in "php.version" setting and the version picker.
Example:
{
"php.executables": {
"8.1-dev": "/opt/private/php",
"latest": "/usr/bin/php"
}
}Usage:
The "php.version" setting is defined within a workspace, and thus can be shared on a source control between more machines and users. Specified version identifier (e.g. "7.4"``,"latest", or `"8.1-dev") is defined by "php.executables" setting which is user-specific, and not shared between users. Each user defines their own executable paths for the same "php.version".