Code Completion
The PHP editor analyses the entire workspace, it determines expressions type, function return type, property type, and local variables type. The inferred type information can be improved by providing further details using PHPDoc comments (see below).
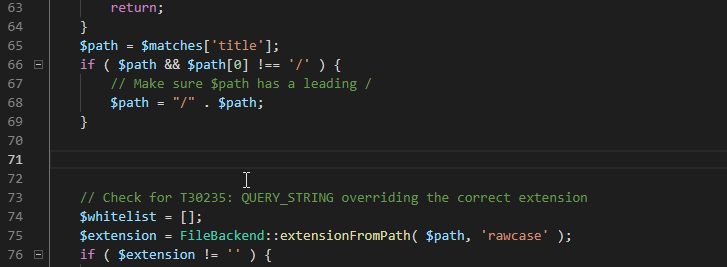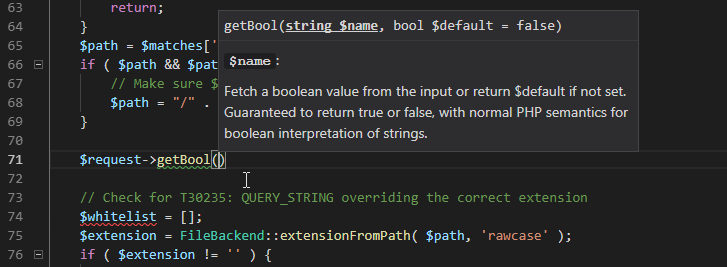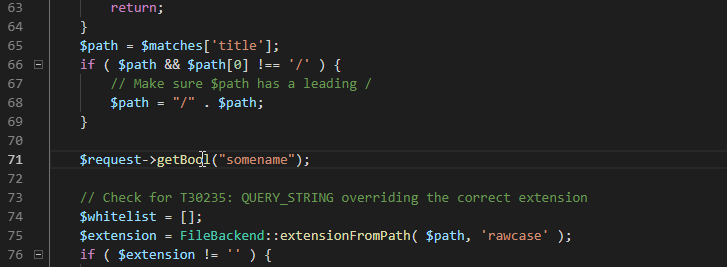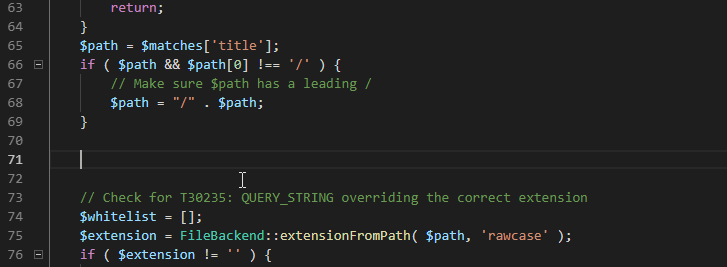
Code completion is context-aware, scope-aware, type-aware, with the respect to conventions and additional heuristics.
Completing Parentheses
By default, completing a function name also completes parentheses and, if the function has any parameters to fill in, the keyboard cursor is placed inside them.
This behavior is controlled by the setting:
"php.completion.parameters": "parentheses"Alternativelly, the editor may complete default values for all the parameters. Set the setting to "parameters" to do so:
"php.completion.parameters": "parameters"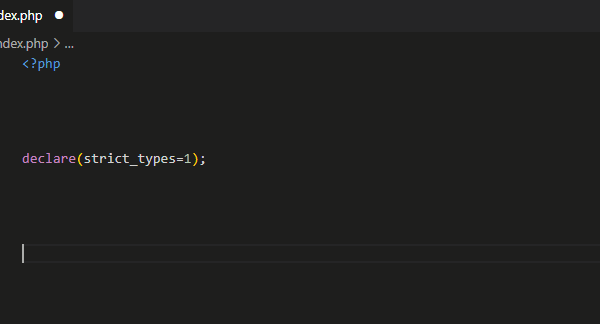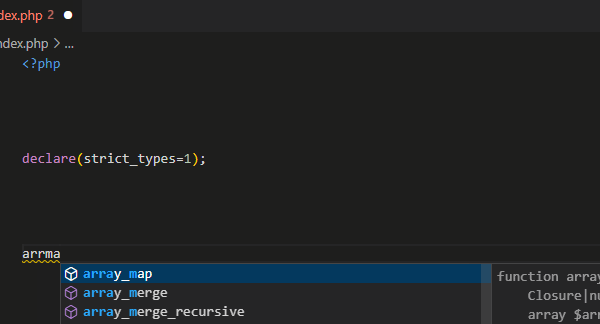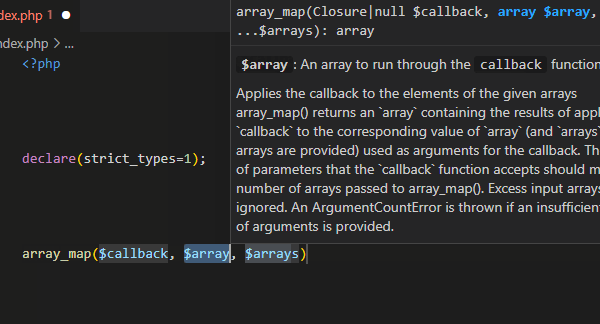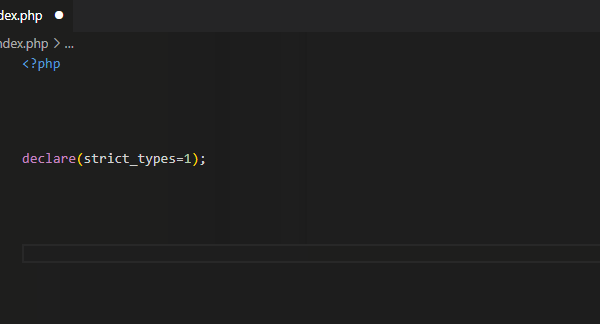
Automatic Triggers
The completion can be triggered manually (Ctrl+Space by default) or automatically. The automatic triggers are:
- a letter completes available symbols in the current context
::after a class/interface/trait name completes the type static members and constants.->after an object instance completes the object's non-static members.\as a part of a qualified name completes the namespaced (qualified) type name.$as a first letter shows variables in the current function scope.- a letter or
Ctrl+Spaceafternewkeyword completes possible class names - a letter or
Ctrl+Spaceafterthrow newcompletes only throwable classes - a letter or
Ctrl+Spaceafterusekeyword. /**above a declaration completes a PHPDoc comment block (needseditor.formatOnTypesetting to be enabled). See PHPDoc Generator for more details.
Additional Information
The editor provides an option to show additional information about the symbol in the code completion list. The information contains the symbol's description as it is written in the corresponding PHPDoc or PHP manual. Additional information may include:
- URL to the corresponding PHP manual Web Site.
- a return value description.
- a Laravel facade accessor.
- a compatibility status, such as a deprecation.
Optimizing Completion
In case variable's or function's type information cannot be inherited, it is advised to provide the expected type in form of a PHPDoc comment. The type hinting works for functions, properties and variables.
An example of type hinting:
class SomeClass
{
/**
* @var array|null
*/
var $property;
/**
* @return SomeClass
*/
function foo()
{
$x = eval('magic1()');
/** @var $x PDOStatement */
$x->query();
return eval('magic2()');
}
}Limitations
The code editor may not resolve class_alias() without constant expressions; therefore some aliased class names may not be included in the code completion.
The code editor won't recognize files containing a syntax error.
The code editor may not provide precise completions after eval() expression or after classes being instantiated indirectly (using an expression new $classname instead of a constant qualified name).