PHP Documentary Comments (PHPDoc)
PHPDoc is a standard way of documenting and annotating the PHP code. It is a well-known format of block comments prefixed with /** characters, and it is used to annotate functions, classes, properties, and also local variables. With PHPDoc it is possible to provide documentation, additional type information, and other information for the editor.
Example
A regular PHPDoc comment looks like the following (in case of a function documentation):
/**
* A short description.
* @param array<int> $a A parameter summary.
* @return int A return value summary.
*/
function foo($a) { ... }In this case it would be placed right above the function declaration in the PHP code. The editor would provide a short description whenever it provides foo code completion, and it would treat the function as it accepts one argument of type array of integers, and returning a value of type integer.
Generate PHPDoc
The PHP Editor automatically generates corresponding PHPDoc stub upon typing /**. This works above functions, classes, interfaces, traits, properties, and constant declarations.
Place caret above function, class, namespace, property, or constant declaration. Type /** and the corresponding PHPDoc block will be generated. The PHP Tools Editor also infers the types and possible exceptions being thrown by the function, so it gets annotated as well.
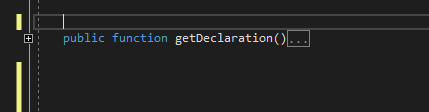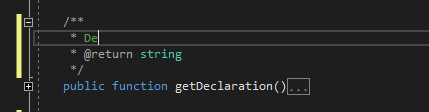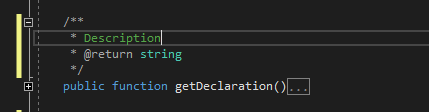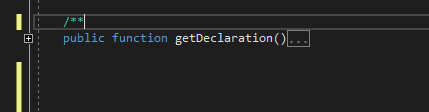
The PHPDoc is inserted as a code snippet with placeholders. Missing information can be filled in. To jump between fields, press TAB.
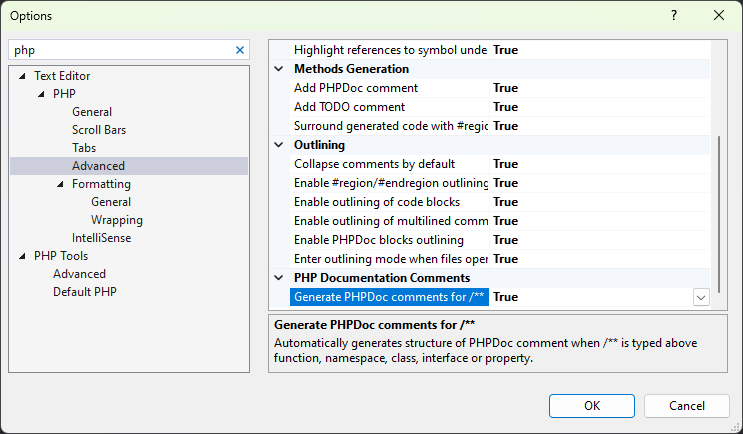
Options
This behavior can be turned off or on (it is on by default) in the Visual Studio's Options window (Tools / Options), in Text Editor / PHP / Advanced, the option Generate PHPDoc comments for /**.
Completing PHPDoc Tags
The PHP Tools Editor provides completion and snippets for PHPDoc tags as well. Place the caret inside PHPDoc block and either type @ or press Ctrl+Space.
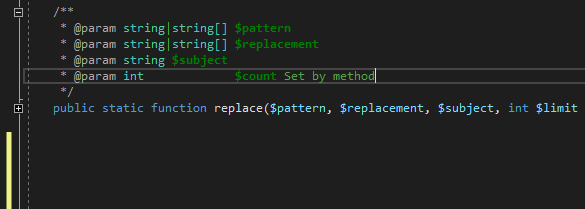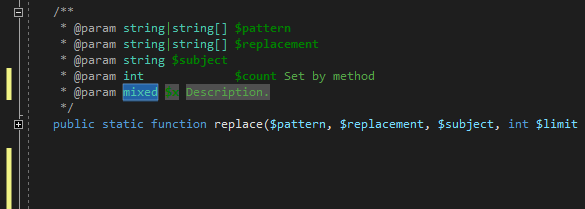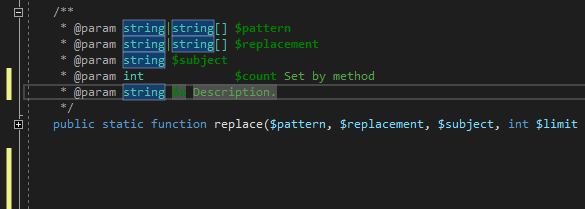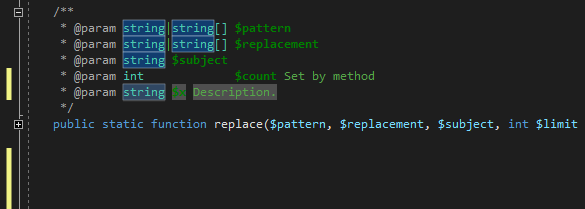
Complete the tag with TAB to insert it as a full snippet, or just confirm the selection to insert the tag name.
Documentation
The text inside the PHPDoc is used for documentation purposes. It can be one or more lines of text. It will be available in quick tool tips, in signature help, or in code completion tool tips.
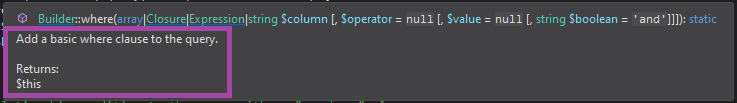
The quick tool tip above shows information from the corresponding PHPDoc comment.
Excluding from IntelliSense
In some cases, the function represents a dummy declaration and is not supposed to be used by developers or being seen in IntelliSense at all. Use @ignore PHPDoc tag to annotate such function.
/** @ignore */
function a_dummy_function() { ... }Example of a function that won't be listed in IntelliSense.
Type Annotations
There are several PHPDoc tags that may be used to annotate the function parameters, function return value, property type, constant type, or a variable type. The standard PHPDoc tags are the following:
@param: specifies the parameter type and description in the form:@param (type) ($name) (description).@return: provides information about the return value in the form:@return (type) (description).@var: allows to annotate properties, constants, class constants:@var (type) (description).@global: annotates global variables within the current scope:@global (type) ($name) (description).
In order to annotate a local variable, the @var tag is used:
/**
* @var MyClass $x The local variable referring to my class.
*/
$x = do_something();The annotation can be placed on a single line as well:
/** @var MyClass $x */Or the variable name can be omitted completely if it can be inferred from the statement below it:
/** @var MyClass */
$x = do_something(); // <-- the editor will know that $x will be MyClass.Generics
The editor understands generic type annotations (also known as templates).
The class/function with template type arguments is annotated with @template PHPDoc tag, optionaly specifying the template type constrain:
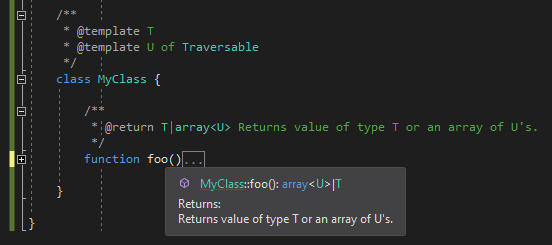
Notice, the tooltip for class MyClass shows the template arguments as well. The type constrain Traversable is used whenever the type U is not bound (whenever the editor does not know the actual assigned type), so it can provide code analytics and code completion.
In order to use the template type arguments, specify them as any other type within PHPDoc.
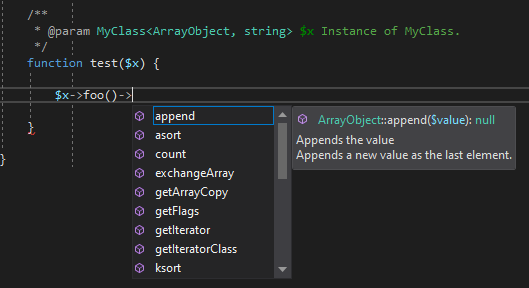
Notice, the editor will substitute T with ArrayObject and U with string. This results in working code completion, and the editor will properly provides completion after foo() which is expected to return either ArrayObject or array<string>.
Psalm/PHPStan
The 3rd party code linters like Psalm or PHPStan introduce extended PHPDoc type annotations. Those are supported by the PHP Tools Editor as well.
Types can be specified in various forms including:
callable(mixed...):(Option<T>)array<int, mixed>array-keynon-empty-stringclass-stringclass-string<T>
PHPDoc tags may be prefixed with @psalm- or @phpstan-. Such tags are handled as well.
The editor respects those annotations but may not take the full advantage of them (yet).
Class Annotations
There are several PHPDoc tag specific to class/interface declartion.
@extendsallows to describe the base class name including its generic type arguments. Example:@extends ArrayObject<int, MyUser>@implementsallows to describe an implemented interface with its generic type arguments. Example:@implements Iterable<int>@useis used above a trait use to describe its generic type arguments.@methoddeclares a method in case the class provides dynamic methods through magic__call()function. This information is used by the code completion to provide this additional method in the list.@propertysimilarly to@methodallows to define a dynamic property.@mixintells the editor to include members of another type (aka mixin) into this class.
Code Validation
The PHPDoc is validated for valid type names, valid tag names, and common typos.
For the quick fixes there are same rules as for the PHP code; invalid type names may get completed namespace. In case the type name is ambiguous or needs to get fully qualified, the \ prefix may get inserted by the code completion or by the quick fix.
Formatting
The PHPDoc comment block is formatted according to the statement below which it corresponds with. The block is formatted according to standards, indented.